일반
| 바이오프린팅 신기술 최초 개발(World’s First Real-Time Elasticity Monitoring-Based Bioprinting Technology) | |||
| 작성일 | 2025-03-06 | 조회수 | 380 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 첨부파일 | |||
|
국립부경대 남승윤 교수팀, 탄성 측정 기반 바이오프린팅 기술 개발 - 세계 최초 실시간 탄성 모니터링 적용 바이오프린팅 기술 개발 성공
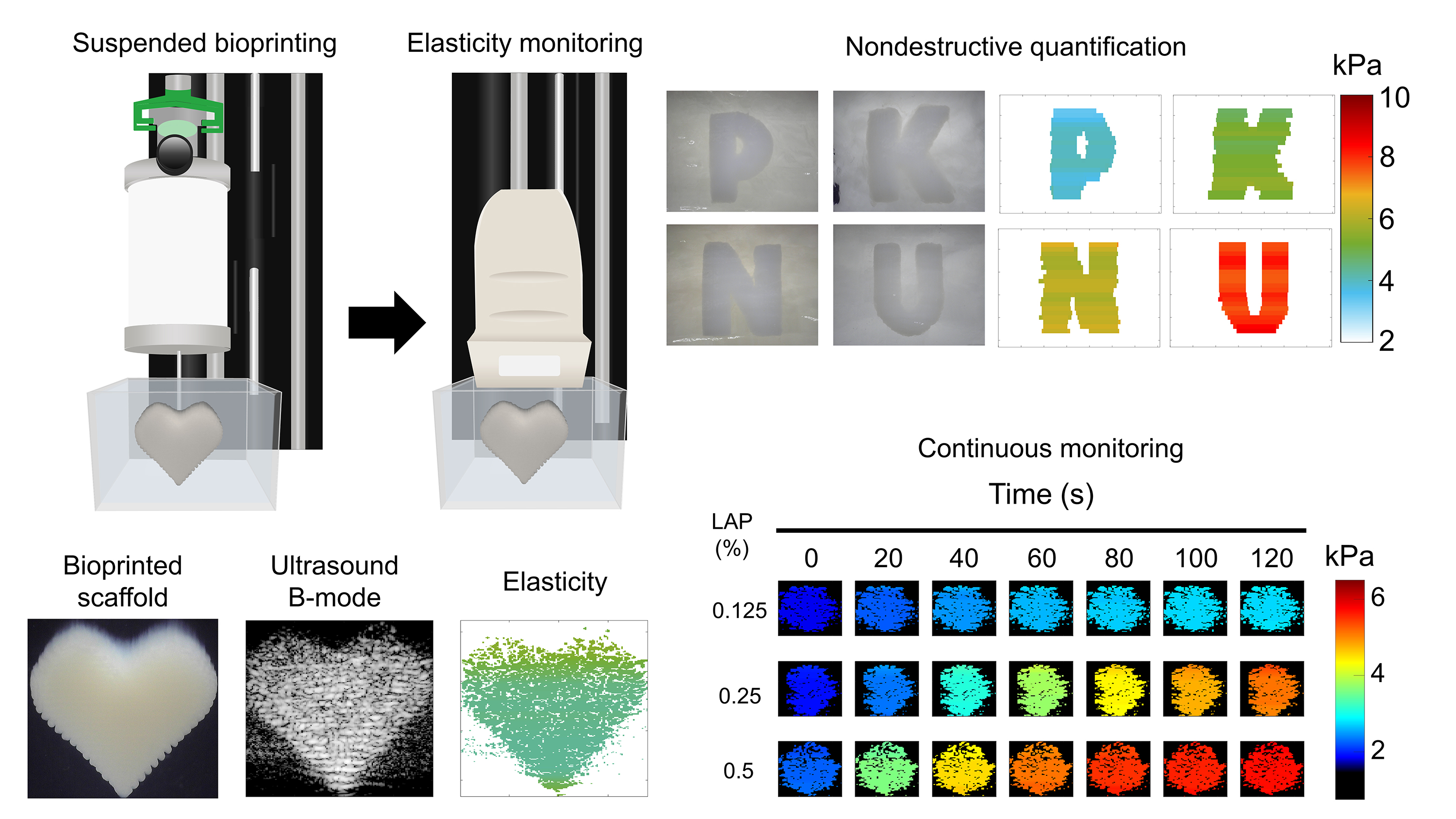
△ 탄성 모니터링 기반 바이오프린팅 과정 및 결과 이미지
국립부경대학교(총장 배상훈)는 스마트헬스케어학부 의공학전공 남승윤 교수 연구팀이 초음파 탄성 모니터링을 활용한 새로운 바이오프린팅 기술을 개발했다고 밝혔다.
남승윤 교수와 같은 학과 박상혁 교수, 인제대학교 의공학부 윤창한 교수 등 공동 연구팀은 바이오프린팅 과정에서 초음파 전단파를 활용, 세포 지지체의 탄성 변화를 실시간으로 정밀하게 측정하는 기술을 처음으로 개발하는 데 성공했다.
바이오프린팅은 인체 조직의 재생과 인공장기 개발에 활용되는 첨단 기술로 개발 중이지만, 제작된 세포 지지체의 기계적 특성을 실시간으로 정밀하게 평가하는 데에는 한계가 있다.
인체 조직은 부위마다 탄성이 다양한데, 세포의 생장과 분화가 이러한 기계적 특성에 의해 크게 영향을 받기 때문에 이를 동적으로 모니터링하는 기술 개발이 필수적이다.
기존 기법은 세포 지지체 제작 전후에만 파괴적으로 기계적 특성을 확인할 수 있어 바이오프린팅 과정 중 동적인 변화를 포착하기 어려웠지만, 연구팀이 이번에 개발한 기술은 세포 지지체 제작 중에도 구조의 탄성과 안정성을 비파괴적으로 모니터링할 수 있다는 장점이 있다.
연구팀은 이번 연구 결과를 담은 논문 ‘Suspended bioprinting with in-situ elasticity monitoring using the assessment of shear wave phase velocity’를 제조 분야 최상위급 국제학술지
남승윤 교수는 “이번 연구는 바이오프린팅 분야에서 품질 관리 및 공정 개선을 위한 핵심 기술로 자리 잡을 수 있을 것으로 기대한다. 특히 동일 샘플에 대해 기계적 특성 변화를 장기간, 실시간으로 추적하여 측정오차를 줄이고 경제성을 높일 수 있어 조직공학, 생체재료 관련 분야의 혁신적 발전에 기여할 것.”이라고 밝혔다.
한편, 이번 연구는 보건복지부 인체이식용 생체소재 기술개발사업(RS-2022-KH129323, 연구책임자 서울대학교병원 정은재 교수) 등의 지원을 받아 수행됐다. <부경투데이>
△연구팀 사진(왼쪽부터 김가린, 박상혁, 윤창한, 남승윤)
Pukyong National University Professor Nam Seung Yun’s Team Develops Elasticity Monitoring-Based Bioprinting Technology - World’s First Real-Time Elasticity Monitoring-Based Bioprinting Technology
Pukyong National University (President Bae Sang-Hoon) announced that the research team led by Professor Nam Seung Yun of the Department of Biomedical Engineering has developed a new bioprinting technology using ultrasound elasticity monitoring.
Professor Nam Seung Yun, along with Professor Park Sang-Hyug from the same department and Professor Yoon Changhan from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Inje University, successfully developed the world’s first technology that precisely measures the elasticity changes of cell scaffolds in real-time during the bioprinting process using ultrasonic shear wave elastography.
Bioprinting is an advanced technology for tissue regeneration and artificial organ development, but there have been limitations in precisely evaluating the mechanical properties of cell scaffolds in real time.
Human tissues have varying elastic properties, and since the growth and differentiation of cells are greatly influenced by these mechanical characteristics, the development of a technology to dynamically monitor them is essential.
Conventional methods can only assess the mechanical properties destructively before and after the fabrication of the cell scaffold, making it difficult to capture dynamic changes during the bioprinting process. However, the technology developed by the research team has the advantage of enabling non-destructive monitoring of the elasticity and stability of the structure even during the fabrication of the cell scaffolds.
The research team published their findings in the paper titled “Suspended bioprinting with in-situ elasticity monitoring using the assessment of shear wave phase velocity” in the top-tier international journal
Professor Nam Seung Yun stated, “This research is expected to serve as a key technology for quality control and process optimization in the field of bioprinting. In particular, by enabling long-term tracking and measurement of mechanical property changes in real time for the same sample, it can reduce measurement errors and enhance cost-effectiveness, contributing to innovative advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Health and Welfare’s Project of Biomaterial Development for Human Implantation (RS-2022-KH129323, principal investigator: Professor Chung Eun-Jae at Seoul National University Hospital). <관련링크> |
|||
| 다음 | 2024학년도 의공학전공 홈커밍데이 |
|---|---|
| 이전 | 패 유래 물질 항암·항균 연구 '주목'(Research on Anti-Cancer and Anti-Bacterial Properties of Phytonutrients Gains ‘Attention’) |